Scientists seized the evidence of intestinal bacteria "doing evil" in another Science paper published on the same day!

Science(DOI: 10.1126/science.aar7201)
In recent years, more and more research shows that the intestinal bacteria living in the human body are related to a series of diseases, including the immune system attacking autoimmune diseases of healthy tissues. To clarify this connection, a research team at Yale focused on a bacterium called Enterococcus gallinarum. It was found that the bacteria could spontaneously metastasize to the outside of the intestine and enter the lymph nodes, liver and spleen.
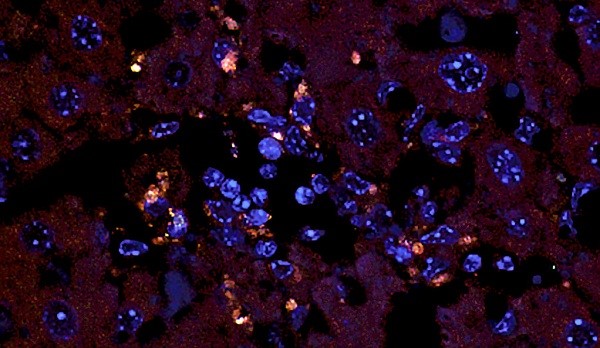
Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) image of the gut commensal E. gallinarum translocated into the liver tissue of autoimmune mice. Orange dots represent the bacterium. Credit: Manfredo Vieira et al., Science (2018)
Using a mouse model, the scientists observed that in these tissues outside the gut, E. gallinarum initiates the production of autoantibodies and inflammation, which are all features of the autoimmune response. In healthy individuals cultured hepatocytes, they confirmed the same inflammatory mechanisms. At the same time, studies have found that this bacteria is also present in the liver of patients with autoimmune diseases.
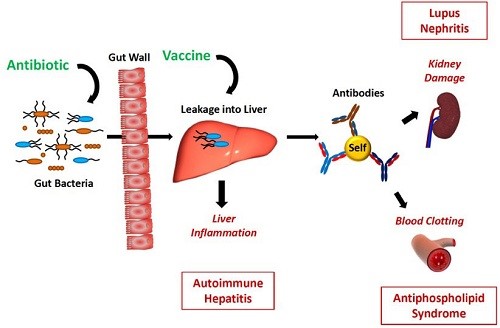
An oral antibiotic or a vaccine into the muscle that is directed against E. gallinarum prevent autoimmune diseases to occur. Credit: Martin Kriegel
Through further experiments, the research team confirmed that mice can be suppressed for autoimmunity with antibiotics or vaccine against E. gallinarum. Using both methods, they can inhibit the growth of bacteria in tissues and weaken their impact on the immune system.
The author of the paper, Corresponding author Dr. Martin Kriegel, said: “The vaccine against E. gallinarum is a special method. Its administration method is intramuscular injection, which is to avoid targeting other bacteria in the intestinal tract. When the blockage leads to inflammation When we arrived, we successfully reversed the effects of E. gallinarum on autoimmunity.”
Kriegel and colleagues plan to further investigate E. gallinarum and its related mechanisms. They believe that the use of antibiotics and other methods (such as vaccines) for treatment are promising ways to improve the lives of patients with autoimmune diseases (such as systemic lupus erythematosus and autoimmune liver disease).
Reference:
The enemy within: Gut bacteria drive autoimmune disease
Souce: NovoPro 2018-03-12
