-
Product Name
VCAM-1 antibody
- Documents
-
Description
VCAM-1 Rabbit Polyclonal antibody. Positive IHC detected in human spleen tissue, human kidney tissue, human lung cancer tissue, human placenta tissue, human tonsillitis tissue.
-
Tested applications
ELISA, IHC
-
Species reactivity
Human,Mouse,Rat; other species not tested.
-
Alternative names
CD106 antibody; DKFZp779G2333 antibody; INCAM 100 antibody; L1CAM antibody; V CAM 1 antibody; VCAM 1 antibody; VCAM1 antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
This antibody was obtained by immunization of VCAM-1 recombinant protein (Accession Number: NM_001078). Purification method: Antigen affinity purified.
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.1% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. DO NOT ALIQUOT
-
Applications
Recommended Dilution:
IHC: 1:20-1:200
-
Validations
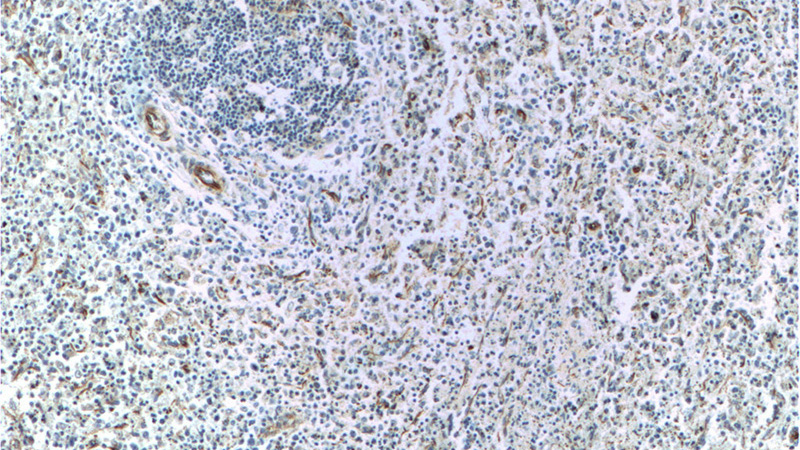
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human spleen tissue slide using Catalog No:116725(VCAM-1 Antibody) at dilution of 1:50 (under 10x lens)
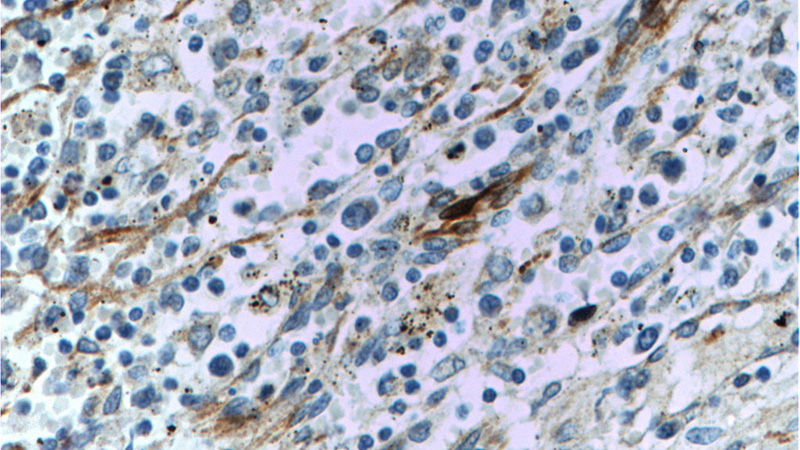
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human spleen tissue slide using Catalog No:116725(VCAM-1 Antibody) at dilution of 1:50 (under 40x lens)
-
Background
Vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM1), also known as CD106, is a transmembrane glycoprotein belonging to the immunoglobulin gene superfamily. VCAM1 is expressed by cytokine-activated endothelium, interacts with integrin VLA4 (α4β1) present on the surface of leukocytes, and mediates both adhesion and signal transduction. It is also expressed either constitutively or inducibly in a variety of other cell types, including vascular smooth muscle cells, differentiating skeletal muscle cells, renal and neural epithelial cells, macrophages (Kupffer cells), dendritic cells, and bone marrow stromal cells (PMID: 7507076, 11359843).
-
References
- Chinthamani S, Odusanwo O, Mondal N, Nelson J, Neelamegham S, Baker OJ. Lipoxin A4 inhibits immune cell binding to salivary epithelium and vascular endothelium. American journal of physiology. Cell physiology. 302(7):C968-78. 2012.
- Cheng HS, Sivachandran N, Lau A. MicroRNA-146 represses endothelial activation by inhibiting pro-inflammatory pathways. EMBO molecular medicine. 5(7):949-66. 2013.
- Jin Y, Liu K, Peng J. Rhizoma Dioscoreae Nipponicae polysaccharides protect HUVECs from H2O2-induced injury by regulating PPARγ factor and the NADPH oxidase/ROS-NF-κB signal pathway. Toxicology letters. 232(1):149-158. 2014.
- Wu S, Xu H, Peng J. Potent anti-inflammatory effect of dioscin mediated by suppression of TNF-α-induced VCAM-1, ICAM-1and EL expression via the NF-κB pathway. Biochimie. 110:62-72. 2015.
- Lehrke M, Kahles F, Makowska A. PDE4 inhibition reduces neointima formation and inhibits VCAM-1 expression and histone methylation in an Epac-dependent manner. Journal of molecular and cellular cardiology. 81:23-33. 2015.
- Liu Y, Yang G, Zhang J. Anti-TNF-α monoclonal antibody reverses psoriasis through dual inhibition of inflammation and angiogenesis. International immunopharmacology. 28(1):731-43. 2015.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
