-
Product Name
MBP-Tag antibody
- Documents
-
Description
MBP-Tag Rabbit Polyclonal antibody. Positive WB detected in lane1: MBP-NOL6 64kd; lane2 MBP 42kd, Recombinant protein.
-
Tested applications
ELISA, WB
-
Species reactivity
Tag
-
Alternative names
Maltose Binding Protein antibody; MBP antibody; MBP Tag antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
This antibody was obtained by immunization of MBP-Tag recombinant protein. Purification method: Antigen affinity purified.
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. DO NOT ALIQUOT
-
Applications
Recommended Dilution:
WB: 1:1000-1:10000
-
Validations
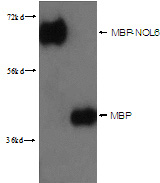
lane1: MBP-NOL6 64kd; lane2 MBP 42kd were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with Catalog No:117331(MBP-Tag Antibody) at dilution of 1:3000
-
Background
Protein tags are protein or peptide sequences located either on the C- or N- terminal of the target protein, which facilitates one or several of the following characteristics: solubility, detection, purification, localization and expression. Maltose binding protein (MBP) is the 370 amino acid product of the E.coli mal E gene. MBP is a useful affinity tag that can increase the expression level and solubility of the resulting tagged protein. The MBP tag also promotes proper folding of the attached protein. Plasmid vectors have been constructed utilizing the MBP domain that allow the synthesis of high levels of MBP-fusion proteins that can be purified in a one step procedure by affinity chromatography cross linked amylose resin. Once bound to amylose, the MBP protein can then be separated from the target protein by cleavage by coagulation Factor Xa at a specific four residue site. Alternatively, the intact fusion protein can be specifically eluted from the resin by the addition of excess free maltose. Subsequent to elution, MBP fusion protein can be visualized either by western blot analysis or immunoprecipitation using antibodies specific for the MBP-tag. This antibody recognizes MBP (Maltose binding protein) TAG in some expression systems.
-
References
- Deng H, Liu H, Li X, Xiao J, Wang S. A CCCH-type zinc finger nucleic acid-binding protein quantitatively confers resistance against rice bacterial blight disease. Plant physiology. 158(2):876-89. 2012.
- Mao G, Lee S, Ortega J, Gu L, Li GM. Modulation of microRNA processing by mismatch repair protein MutLα. Cell research. 22(6):973-85. 2012.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
