-
Product Name
KCNA4 Polyclonal Antibody
- Documents
-
Description
Polyclonal antibody to KCNA4
-
Tested applications
WB
-
Species reactivity
Human
-
Alternative names
KCNA4 antibody; HBK4 antibody; HK1 antibody; HPCN2 antibody; HUKII antibody; KCNA4L antibody; KCNA8 antibody; KV1.4 antibody; PCN2 antibody; potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily A member 4 antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
Antigen: A synthetic peptide of human KCNA4
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, pH7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at 4℃. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles.
-
Applications
WB 1:500 - 1:1000
-
Validations
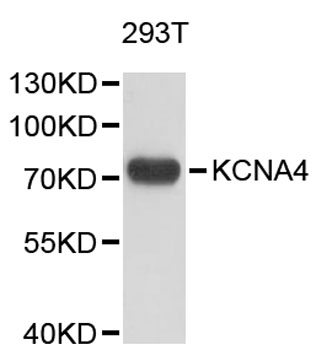
Western blot - KCNA4 Polyclonal Antibody
Western blot analysis of extracts of 293T cells, using KCNA4 antibody .Secondary antibody: HRP Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) at 1:10000 dilution.Lysates/proteins: 25ug per lane.Blocking buffer: 3% nonfat dry milk in TBST.
-
Background
Voltage-gated potassium channel that mediates transmembrane potassium transport in excitable membranes. Forms tetrameric potassium-selective channels through which potassium ions pass in accordance with their electrochemical gradient. The channel alternates between opened and closed conformations in response to the voltage difference across the membrane. Can form functional homotetrameric channels and heterotetrameric channels that contain variable proportions of KCNA1, KCNA2, KCNA4, KCNA5, and possibly other family members as well; channel properties depend on the type of alpha subunits that are part of the channel. Channel properties are modulated by cytoplasmic beta subunits that regulate the subcellular location of the alpha subunits and promote rapid inactivation. In vivo, membranes probably contain a mixture of heteromeric potassium channel complexes, making it difficult to assign currents observed in intact tissues to any particular potassium channel family member. Homotetrameric KCNA4 forms a potassium channel that opens in response to membrane depolarization, followed by rapid spontaneous channel closure. Likewise, a heterotetrameric channel formed by KCNA1 and KCNA4 shows rapid inactivation.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
