-
Product Name
EPHA4 Polyclonal Antibody
- Documents
-
Description
Polyclonal antibody to EPHA4
-
Tested applications
WB
-
Species reactivity
Mouse, Rat
-
Alternative names
EPHA4 antibody; HEK8 antibody; SEK antibody; TYRO1 antibody; EPH receptor A4 antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
Antigen: Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 887-986 of human EPHA4 (NP_004429.1).
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles.
-
Applications
WB 1:500 - 1:2000
-
Validations
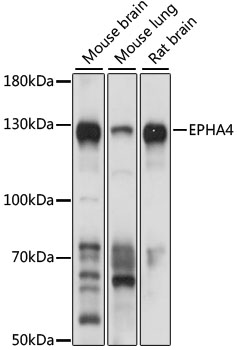
Western blot - EPHA4 Polyclonal Antibody
Western blot analysis of extracts of various cell lines, using EPHA4 antibody at 1:1000 dilution.Secondary antibody: HRP Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) at 1:10000 dilution.Lysates/proteins: 25ug per lane.Blocking buffer: 3% nonfat dry milk in TBST.Detection: ECL Basic Kit .Exposure time: 3s.
-
Background
Receptor tyrosine kinase which binds membrane-bound ephrin family ligands residing on adjacent cells, leading to contact-dependent bidirectional signaling into neighboring cells. The signaling pathway downstream of the receptor is referred to as forward signaling while the signaling pathway downstream of the ephrin ligand is referred to as reverse signaling. Highly promiscuous, it has the unique property among Eph receptors to bind and to be physiologically activated by both GPI-anchored ephrin-A and transmembrane ephrin-B ligands including EFNA1 and EFNB3. Upon activation by ephrin ligands, modulates cell morphology and integrin-dependent cell adhesion through regulation of the Rac, Rap and Rho GTPases activity. Plays an important role in the development of the nervous system controlling different steps of axonal guidance including the establishment of the corticospinal projections. May also control the segregation of motor and sensory axons during neuromuscular circuit development. In addition to its role in axonal guidance plays a role in synaptic plasticity. Activated by EFNA1 phosphorylates CDK5 at 'Tyr-15' which in turn phosphorylates NGEF regulating RHOA and dendritic spine morphogenesis. In the nervous system, plays also a role in repair after injury preventing axonal regeneration and in angiogenesis playing a role in central nervous system vascular formation. Additionally, its promiscuity makes it available to participate in a variety of cell-cell signaling regulating for instance the development of the thymic epithelium.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
