-
Product Name
Anti-RPA32/RPA2 Rabbit antibody
- Documents
-
Description
RPA32/RPA2 Rabbit monoclonal antibody
-
Tested applications
WB, IHC-P, IP
-
Species reactivity
Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Alternative names
REPA2; RPA32; RP-A p32; RP-A p34 antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
Antigen: A synthetic peptide of human RPA32/RPA2
-
Clonality
Monoclonal
-
Formulation
50nM Tris-Glycine(pH 7.4), 0.15M Nacl, 40%Glycerol, 0.01% sodium azide and 0.05% BSA.
-
Storage instructions
Store at 4°C short term. Store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze / thaw cycle.
-
Applications
WB: 1/1000-1/2000
IHC: 1/50-1/200
IP: 1/20
-
Validations
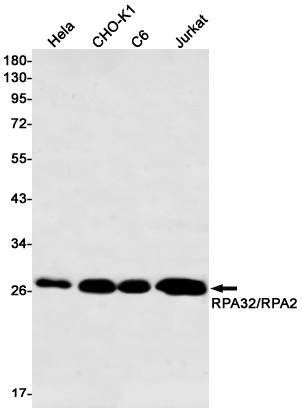
Western blot detection of RPA32/RPA2 in Hela,CHO-K1,C6,Jurkat cell lysates using RPA32/RPA2 Rabbit mAb(1:500 diluted).Predicted band size:29kDa.Observed band size:29kDa.
-
Background
Swiss-Prot Acc.P15927.As part of the heterotrimeric replication protein A complex (RPA/RP-A), binds and stabilizes single-stranded DNA intermediates, that form during DNA replication or upon DNA stress. It prevents their reannealing and in parallel, recruits and activates different proteins and complexes involved in DNA metabolism. Thereby, it plays an essential role both in DNA replication and the cellular response to DNA damage. In the cellular response to DNA damage, the RPA complex controls DNA repair and DNA damage checkpoint activation. Through recruitment of ATRIP activates the ATR kinase a master regulator of the DNA damage response. It is required for the recruitment of the DNA double-strand break repair factors RAD51 and RAD52 to chromatin in response to DNA damage. Also recruits to sites of DNA damage proteins like XPA and XPG that are involved in nucleotide excision repair and is required for this mechanism of DNA repair. Plays also a role in base excision repair (BER) probably through interaction with UNG. Also recruits SMARCAL1/HARP, which is involved in replication fork restart, to sites of DNA damage. May also play a role in telomere maintenance.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
