-
Product Name
UBD antibody
- Documents
-
Description
UBD Rabbit Polyclonal antibody. Positive WB detected in human stomach tissue, Jurkat cells, Raji cells. Positive IHC detected in human colon cancer tissue. Observed molecular weight by Western-blot: 18 kDa
-
Tested applications
ELISA, WB, IHC
-
Species reactivity
Human; other species not tested.
-
Alternative names
Diubiquitin antibody; FAT10 antibody; GABBR1 antibody; UBD antibody; UBD 3 antibody; ubiquitin D antibody; Ubiquitin like protein FAT10 antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
This antibody was obtained by immunization of UBD recombinant protein (Accession Number: NM_006398). Purification method: Antigen affinity purified.
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. DO NOT ALIQUOT
-
Applications
Recommended Dilution:
WB: 1:500-1:5000
IHC: 1:20-1:200
-
Validations
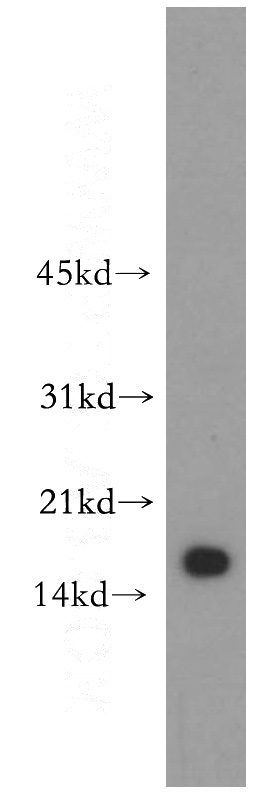
human stomach tissue were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with Catalog No:116512(UBD antibody) at dilution of 1:300
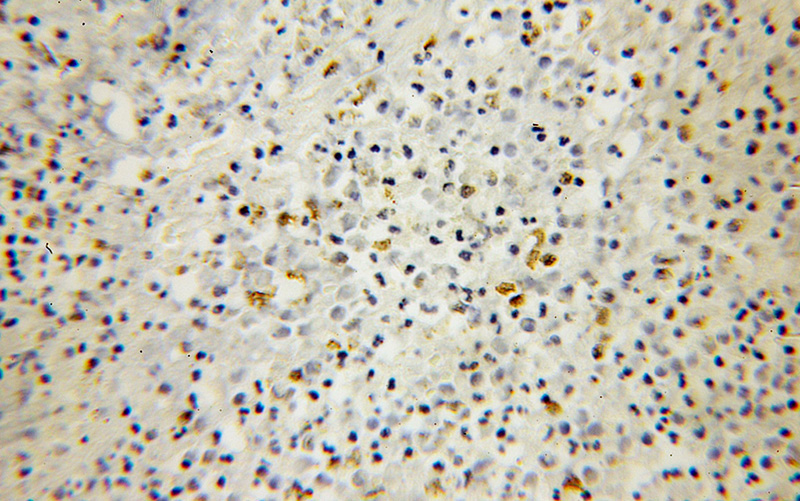
Immunohistochemical of paraffin-embedded human colon cancer using Catalog No:116512(UBD antibody) at dilution of 1:100 (under 10x lens)
-
Background
UBD, also named as FAT10, contains two ubiquitin-like domains. It is a ubiquitin-like protein modifier which can be covalently attached to target protein and subsequently leads to their degradation by the 26S proteasome, in a NUB1L-dependent manner. UBD also has important roles in cell mitosis, chromosome instability, apoptosis and immune response. UBD mediates apoptosis in a caspase-dependent manner, especially in renal epithelium and tubular cells during renal diseases such as polycystic kidney disease and Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-associated nephropathy (HIVAN). It promotes the expression of the proteasome subunit beta type-9 (PSMB9/LMP2). UBD regulates TNF-alpha-induced and LPS-mediated activation of the central mediator of innate immunity NF-kappa-B by promoting TNF-alpha-mediated proteasomal degradation of ubiquitinated-I-kappa-B-alpha. It may be involved in dendritic cell (DC) maturation, the process by which immature dendritic cells differentiate into fully competent antigen-presenting cells that initiate T cell responses. UBD may be a marker for precancerous lesions and may promote cancer progression. This antibody is a rabbit polyclonal antibody raised against full length UBD of human origin.
-
References
- Kobayashi A, Donaldson DS, Kanaya T. Identification of novel genes selectively expressed in the follicle-associated epithelium from the meta-analysis of transcriptomics data from multiple mouse cell and tissue populations. DNA research : an international journal for rapid publication of reports on genes and genomes. 19(5):407-22. 2012.
- Taniai E, Yafune A, Nakajima M. Ochratoxin A induces karyomegaly and cell cycle aberrations in renal tubular cells without relation to induction of oxidative stress responses in rats. Toxicology letters. 224(1):64-72. 2014.
- Kimura M, Abe H, Mizukami S. Onset of hepatocarcinogen-specific cell proliferation and cell cycle aberration during the early stage of repeated hepatocarcinogen administration in rats. Journal of applied toxicology : JAT. 36(2):223-37. 2016.
- Kimura M, Mizukami S, Watanabe Y. Disruption of spindle checkpoint function ahead of facilitation of cell proliferation by repeated administration of hepatocarcinogens in rats. The Journal of toxicological sciences. 40(6):855-71. 2015.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
