-
Product Name
SNAI1 antibody
- Documents
-
Description
SNAI1 Rabbit Polyclonal antibody. Positive WB detected in mouse kidney tissue, COLO 320 cells, HeLa cells, human heart tissue, mouse heart tissue, NIH/3T3 cells. Positive IP detected in MCF-7 cells. Positive IHC detected in human kidney tissue. Observed molecular weight by Western-blot: 29 kDa
-
Tested applications
ELISA, WB, IHC, IP
-
Species reactivity
Human,Mouse,Rat; other species not tested.
-
Alternative names
dJ710H13.1 antibody; Protein sna antibody; Protein snail homolog 1 antibody; SLUGH2 antibody; SNA antibody; SNAH antibody; SNAI1 antibody; snail homolog 1 (Drosophila) antibody; SNAIL1 antibody; Zinc finger protein SNAI1 antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
This antibody was obtained by immunization of SNAI1 recombinant protein (Accession Number: NM_005985). Purification method: Antigen affinity purified.
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.1% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. DO NOT ALIQUOT
-
Applications
Recommended Dilution:
WB: 1:500-1:5000
IP: 1:200-1:2000
IHC: 1:20-1:200
-
Validations

mouse kidney tissue were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with Catalog No:115441(SNAI1 antibody) at dilution of 1:1000
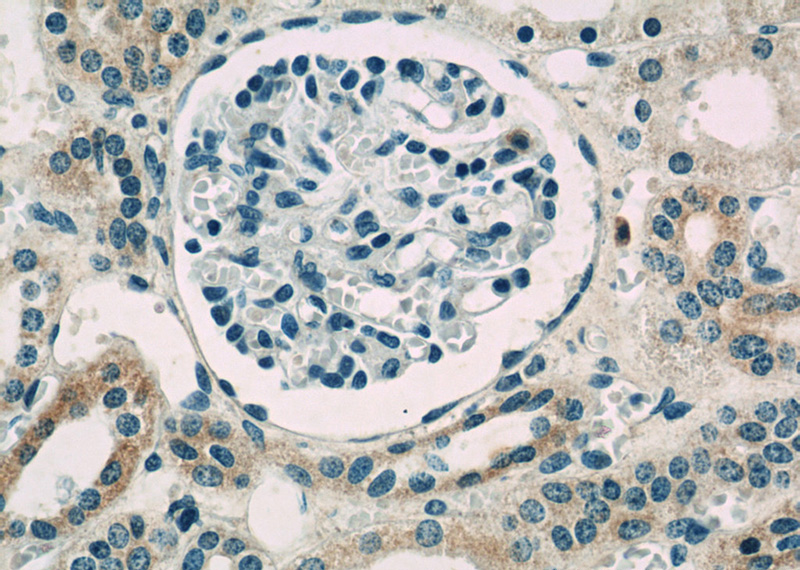
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human kidney slide using Catalog No:115441(SNAI1 Antibody) at dilution of 1:50
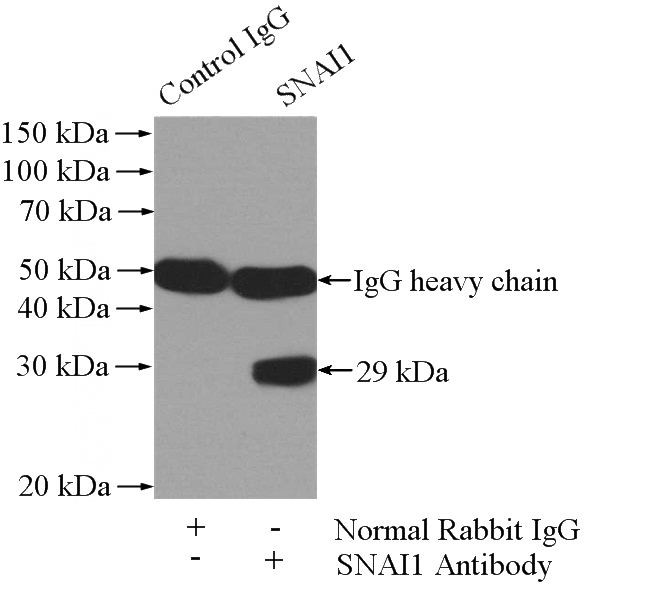
IP Result of anti-SNAI1 (IP:Catalog No:115441, 4ug; Detection:Catalog No:115441 1:600) with MCF-7 cells lysate 1040ug.
-
Background
SNAI1, a member of SNAI1 family of protein, participates in the epithelial to mesenchymal transition(EMT) and formation and maintenance of embryonic mesoderm. The snail family share a common structural, that a highly conserved C-terminal region containing a zinc finger transcription factor. SNAI1 interacts with other corepressor, such as Ajuba, PRMT5 and SIN3a or HDAC1 and 2, to repress the target gene.
-
References
- Magnusson C, Bengtsson AM, Liu M. Regulation of cysteinyl leukotriene receptor 2 expression--a potential anti-tumor mechanism. PloS one. 6(12):e29060. 2011.
- Ding J, Jin W, Chen C, Shao Z, Wu J. Tumor associated macrophage × cancer cell hybrids may acquire cancer stem cell properties in breast cancer. PloS one. 7(7):e41942. 2012.
- Song Q, Xu Y, Yang C. miR-483-5p promotes invasion and metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma by targeting RhoGDI1 and ALCAM. Cancer research. 74(11):3031-42. 2014.
- Miao L, Xiong X, Lin Y. miR-203 inhibits tumor cell migration and invasion via caveolin-1 in pancreatic cancer cells. Oncology letters. 7(3):658-662. 2014.
- Luo BH, Xiong F, Wang JP. Epidermal growth factor-like domain-containing protein 7 (EGFL7) enhances EGF receptor-AKT signaling, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, and metastasis of gastric cancer cells. PloS one. 9(6):e99922. 2014.
- Shao S, Zhao X, Zhang X. Notch1 signaling regulates the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and invasion of breast cancer in a Slug-dependent manner. Molecular cancer. 14:28. 2015.
- Wang P, Cheng H, Wu J, Yan A, Zhang L. STK33 plays an important positive role in the development of human large cell lung cancers with variable metastatic potential. Acta biochimica et biophysica Sinica. 47(3):214-23. 2015.
- Huang W, Liu J, Feng X. DLC-1 induces mitochondrial apoptosis and epithelial mesenchymal transition arrest in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by targeting EGFR/Akt/NF-κB pathway. Medical oncology (Northwood, London, England). 32(4):115. 2015.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
