-
Product Name
HMGB1 antibody
- Documents
-
Description
HMGB1 Rabbit Polyclonal antibody. Positive WB detected in Jurkat cells, COLO 320 cells, HEK-293 cells, human brain tissue, human testis tissue, mouse brain tissue, mouse kidney tissue, rat brain tissue, rat stomach tissue. Positive IP detected in HepG2 cells. Positive IHC detected in human breast cancer tissue. Observed molecular weight by Western-blot: 30kd
-
Tested applications
ELISA, WB, IHC, IP
-
Species reactivity
Human,Mouse,Rat; other species not tested.
-
Alternative names
DKFZp686A04236 antibody; high mobility group box 1 antibody; High mobility group protein 1 antibody; High mobility group protein B1 antibody; HMG 1 antibody; HMG1 antibody; HMG3 antibody; HMGB1 antibody; SBP 1 antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
This antibody was obtained by immunization of HMGB1 recombinant protein (Accession Number: NM_001370340). Purification method: Antigen affinity purified.
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.1% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. DO NOT ALIQUOT
-
Applications
Recommended Dilution:
WB: 1:500-1:5000
IP: 1:200-1:2000
IHC: 1:20-1:200
-
Validations
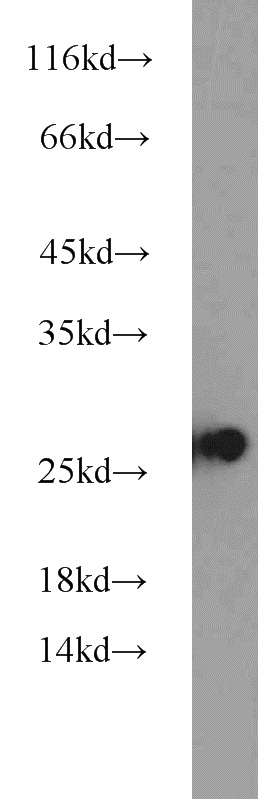
Jurkat cells were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with Catalog No:111478(HMGB1 antibody) at dilution of 1:1000
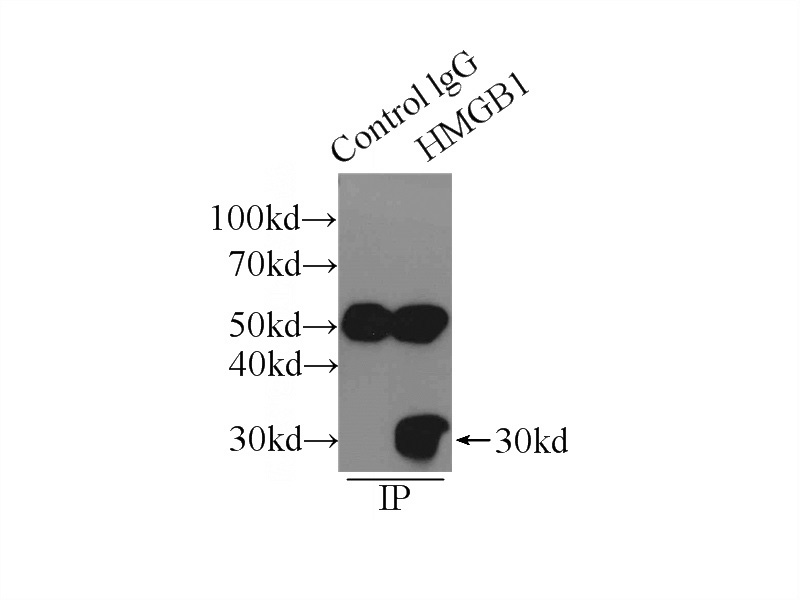
IP Result of anti-HMGB1 (IP:Catalog No:111478, 3ug; Detection:Catalog No:111478 1:500) with HepG2 cells lysate 2900ug.
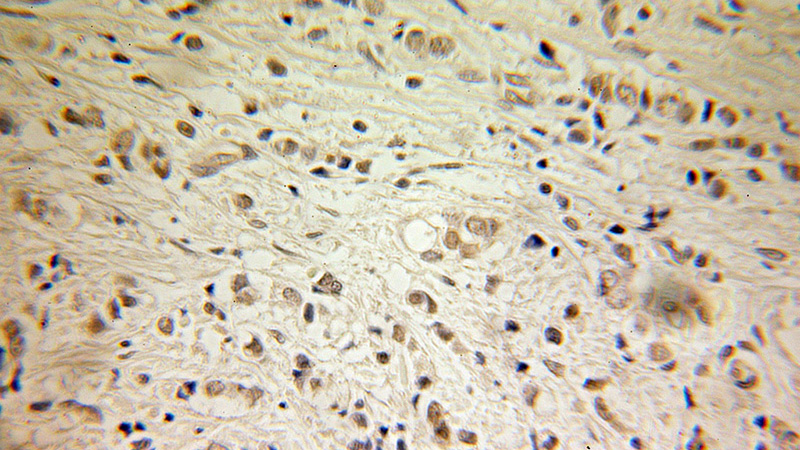
Immunohistochemical of paraffin-embedded human breast cancer using Catalog No:111478(HMGB1 antibody) at dilution of 1:100 (under 10x lens)
-
Background
The HMG (high mobility group) proteins are nonhistone chromosomal proteins that is present in almost all eukaryotic cells, and it functions to stabilize NUCLEOSOME formation and acts as a transcription-factor-like protein that regulates the expression of several genes[PMID: 18160415]. Once injury, infection or other inflammatory stimuli, activated macrophages, mature dendritic cells and natural killer cells can secret HMGB1, which act as a crucial cytokine[PMID: 20163887]. HMGB1 also involved in V(D)J recombination by acting as a cofactor of the RAG complex, stimulating cleavage and RAG protein binding at the 23 bp spacer of conserved recombination signal sequences (RSS)[PMID: 19360789 ]. Act as a Heparin-binding protein that has a role in the extension of neurite-type cytoplasmic processes in developing cells. HMGB1 (high mobility group box 1) modulates gene expression in the nucleus, but certain immune cells secrete HMGB1 as an extracellular Alarmin to signal tissue damage.The nuclear HMGB1 relocalizes to the extracellular milieu in senescent human and mouse cells in culture and in vivo, which stimulated cytokine secretion through TLR-4 signaling (23649808).This antibody is a rabbit polyclonal antibody raised against full length HMGB1 of human origin.
-
References
- Yu M, Wang J, Li W. Proteomic screen defines the hepatocyte nuclear factor 1alpha-binding partners and identifies HMGB1 as a new cofactor of HNF1alpha. Nucleic acids research. 36(4):1209-19. 2008.
- Yu HT, Yu M, Li CY. Specific expression and regulation of hepassocin in the liver and down-regulation of the correlation of HNF1alpha with decreased levels of hepassocin in human hepatocellular carcinoma. The Journal of biological chemistry. 284(20):13335-47. 2009.
- Luan ZG, Zhang H, Yang PT, Ma XC, Zhang C, Guo RX. HMGB1 activates nuclear factor-κB signaling by RAGE and increases the production of TNF-α in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Immunobiology. 215(12):956-62. 2010.
- Abreu MM, Sealy L. The C/EBPbeta isoform, liver-inhibitory protein (LIP), induces autophagy in breast cancer cell lines. Experimental cell research. 316(19):3227-38. 2010.
- DiNorcia J, Moroziewicz DN, Ippagunta N. RAGE signaling significantly impacts tumorigenesis and hepatic tumor growth in murine models of colorectal carcinoma. Journal of gastrointestinal surgery : official journal of the Society for Surgery of the Alimentary Tract. 14(11):1680-90. 2010.
- DiNorcia J, Lee MK, Moroziewicz DN. RAGE gene deletion inhibits the development and progression of ductal neoplasia and prolongs survival in a murine model of pancreatic cancer. Journal of gastrointestinal surgery : official journal of the Society for Surgery of the Alimentary Tract. 16(1):104-12; discussion 112. 2012.
- Davalos AR, Kawahara M, Malhotra GK. p53-dependent release of Alarmin HMGB1 is a central mediator of senescent phenotypes. The Journal of cell biology. 201(4):613-29. 2013.
- Rosu-Myles M, She YM, Fair J. Identification of a candidate proteomic signature to discriminate multipotent and non-multipotent stromal cells. PloS one. 7(6):e38954. 2012.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
