-
Product Name
Cytokeratin 15 antibody
- Documents
-
Description
Cytokeratin 15 Rabbit Polyclonal antibody. Positive IHC detected in human oesophagus cancer tissue, human breast cancer tissue, human cervical cancer tissue, human skin tissue. Positive IP detected in A431 cells. Positive WB detected in mouse thymus tissue. Observed molecular weight by Western-blot: 49 kDa
-
Tested applications
ELISA, WB, IP, IHC
-
Species reactivity
Human,Mouse,Rat; other species not tested.
-
Alternative names
CK 15 antibody; CK15 antibody; Cytokeratin 15 antibody; K15 antibody; K1CO antibody; keratin 15 antibody; KRT15 antibody; KRTB antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
This antibody was obtained by immunization of Cytokeratin 15 recombinant protein (Accession Number: NM_002275). Purification method: Antigen affinity purified.
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.1% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. DO NOT ALIQUOT
-
Applications
Recommended Dilution:
WB: 1:200-1:2000
IP: 1:200-1:2000
IHC: 1:20-1:200
-
Validations
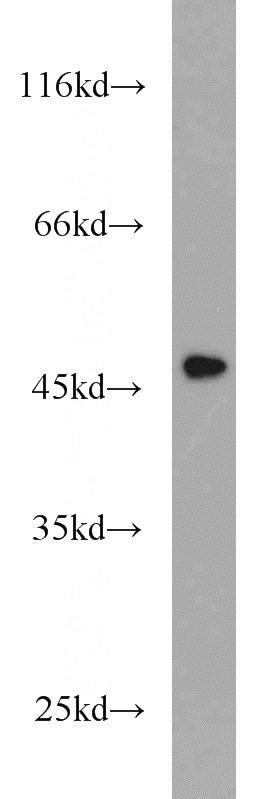
mouse thymus tissue were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with Catalog No:109794(KRT15 antibody) at dilution of 1:500
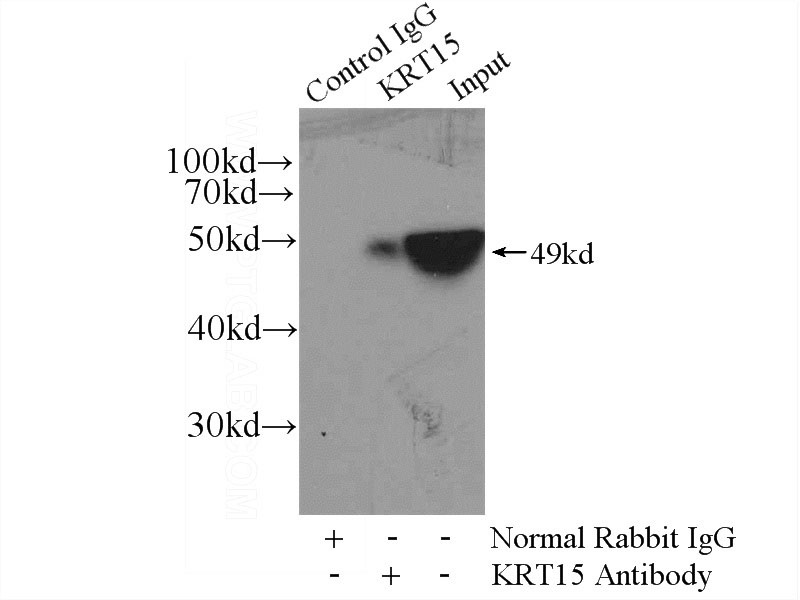
IP Result of anti-KRT15 (IP:Catalog No:109794, 4ug; Detection:Catalog No:109794 1:500) with A431 cells lysate 3040ug.
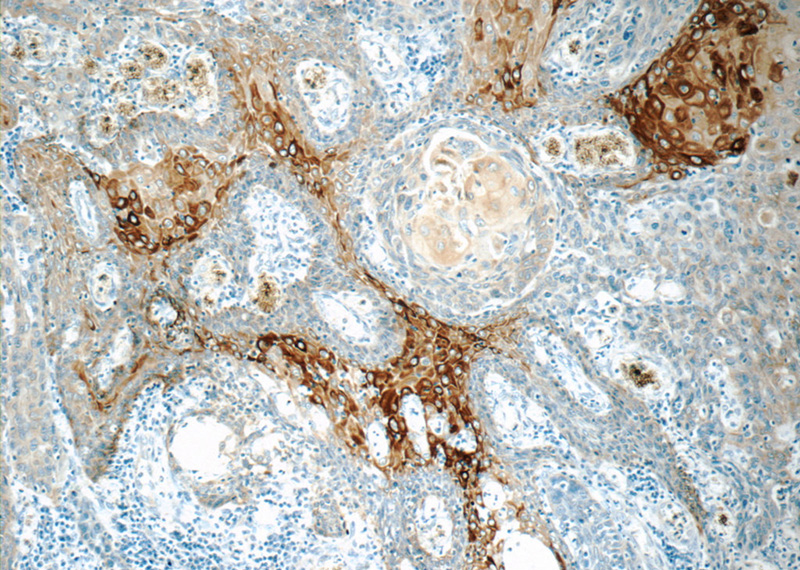
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human oesophagus cancer tissue slide using Catalog No:109794(KRT15 Antibody) at dilution of 1:50 (under 10x lens)
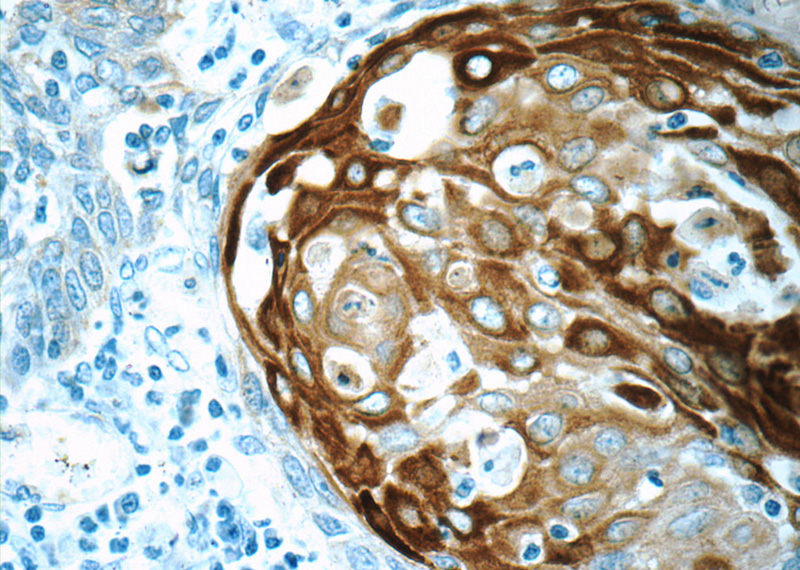
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human oesophagus cancer tissue slide using Catalog No:109794(KRT15 Antibody) at dilution of 1:50 (under 40x lens)
-
Background
Keratins are a large family of proteins that form the intermediate filament cytoskeleton of epithelial cells, which are classified into two major sequence types. Type I keratins are a group of acidic intermediate filament proteins, including K9–K23, and the hair keratins Ha1–Ha8. Type II keratins are the basic or neutral courterparts to the acidic type I keratins, including K1–K8, and the hair keratins, Hb1–Hb6. Keratin 15 is a type I cytokeratin. It is found in some progenitor basal cells within complex epithelia.
-
References
- Zee JM, Shideler KK, Eystathioy T, Bruecks AK, Fritzler MJ, Mydlarski PR. GW bodies: cytoplasmic compartments in normal human skin. The Journal of investigative dermatology. 128(12):2909-12. 2008.
- Zhang W, Zhao J, Chen L, Urbanowicz MM, Nagasaki T. Abnormal epithelial homeostasis in the cornea of mice with a destrin deletion. Molecular vision. 14:1929-39. 2008.
- Zhao J, Mo V, Nagasaki T. Distribution of label-retaining cells in the limbal epithelium of a mouse eye. The journal of histochemistry and cytochemistry : official journal of the Histochemistry Society. 57(2):177-85. 2009.
- Adhikary G, Grun D, Kerr C. Identification of a population of epidermal squamous cell carcinoma cells with enhanced potential for tumor formation. PloS one. 8(12):e84324. 2013.
- Adhikary G, Grun D, Balasubramanian S, Kerr C, Huang JM, Eckert RL. Survival of skin cancer stem cells requires the Ezh2 polycomb group protein. Carcinogenesis. 36(7):800-10. 2015.
- Sartaj R, Chee RI, Yang J. LIM Homeobox Domain 2 Is Required for Corneal Epithelial Homeostasis. Stem cells (Dayton, Ohio). 34(2):493-503. 2016.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
